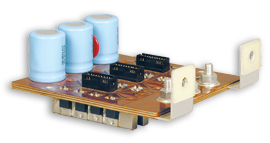
High Current Inverter
A laminated bus bar assembly consisting of three power layers and one signal layer with a total of 59 conductors providing a very low inductance power path and complete gate drive circuitry all designed for a wave-solder assembly process. This bus bar is used in a system powered by 24 MOSFETs, and includes Electrolytic Capacitors, heatsinks and MOVs.
Size: 5” x 7” | Conductors: .060” (gate circuit: .025”) | Volts: 28VDC | Current: 1000A peak
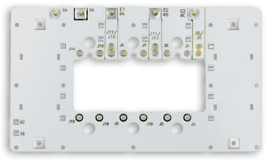
Spacecraft Power Inverter
High current circuit board design using laminated technology for IGBTs and support components. Includes gold plating, quick connect mounting. This laminated bus bar is an enhanced designed of a typical IGBT bus bar. Manufactured to be easily serviced, the design uses gold high current sockets, which are soldered into the DC layers. The design also accommodates resistors and MOVs, soldered right into the assembly. Completely edge filled perimeter, the bus bar also has insulated mounting holes.
Size: 6” x 12” | Thickness: .040” | Voltage: 220V | Current: 75A

Mounting Structure for Capacitor Bank
Laminated bus bars provide a low inductance connection for capacitors. The assembly was designed for an automated production process and the assembly is the DC capacitor bank used in conjunction with high current, high speed switching applications. Positive and negative layers are formed and laminated without outside insulation. This design includes two rows of capacitors soldered into position.
Size: 8” x 8” | Conductors: .030” | Voltage: 63VDC | Current: 300A

Medical Imaging
This space-saving design incorporates five conductors in two layers with clinch hardware at each end. Its laminated, edge-sealed construction is formed to stay out of the way within a tightly packaged medical testing device.
Size: 7” x 8” | Voltages: 3.3V, 5V, 12V | Current: 75A | Conductors: .040”

Compact IGBT Bus Bar
This unique laminated IGBT bus bar delivers low-inductance DC power within a confined area. The design also includes six separate bus bars arranged as AC output with in-line diode connections.
Size: 4” x 19” | Conductors: .050” | Volts: 600VDC/150VAC | Current: .120A (DC)/220A (AC)

Frequency Inverter Bus Bar
An excellent layout containing two large DC bus bars, along with the three AC output bus bars laminated directly on top making a complete laminated power distribution system all under a single part number. Note the inclusion of Faston® tabs for current sensing and press-fit studs for balancing resistors.
Size: 13” x 18” | Current: 820A | Voltage: 550VDC | Conductors: .060” & .125”

High-Frequency Welding
Connecting a complex network including Power IGBTs, Diodes, Resistors, and Film Capacitors, this multi-layer epoxy edge-filled bus bar provides a compact low inductance solution. Thirty-two bushings are brazed into position and maintain tightly controlled coplanar mounting surfaces on both top and bottom. Alternating the plus and minus layers throughout the assembly counters the skin effect of high frequencies.
Size: 5” x 9” | Voltage: 115VDC | Current: 125A | Thickness: .030” & .060”
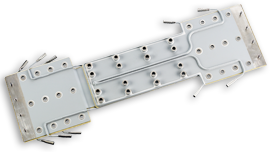
High Frequency Inverter
High frequency applications present a unique thermal challenge requiring the addition of water-cooling for efficient operation. When thermal considerations exceed conventional means of heat dissipation, one option is to add water-cooling to the system. This design contains five cooling lines soldered directly on to the epoxy powder coated conductors to maintain a constant temperature. Due to the high frequency of the AC voltage, “skin effect” plays a big role in the heat created from the bus and without this additional cooling, the bus would surely overheat.

